By A Mystery Man Writer

Immortalized Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells have been obtained immortalizing primary human bladder smooth muscle cells with SV40 Large T antigen
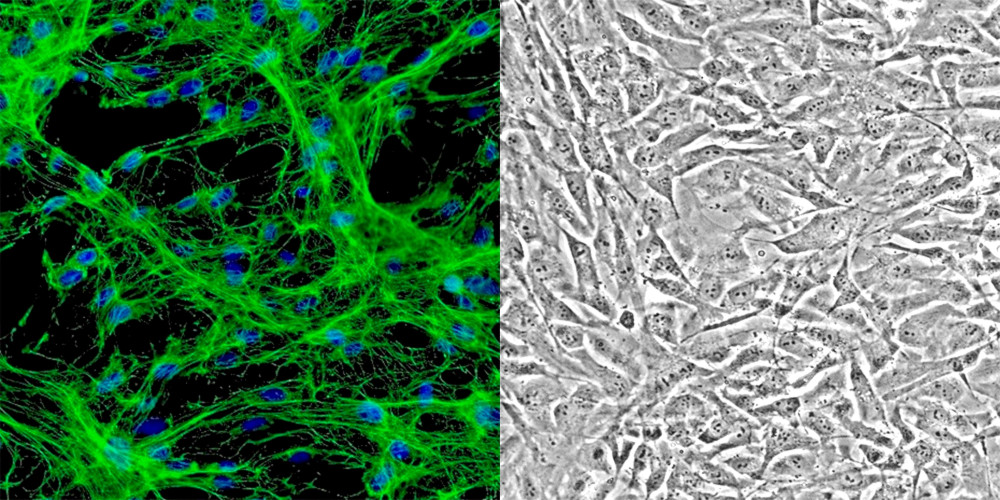
Immortalized Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells (IM-HBlSMC) provided by Innoprot have been developed by immortalizing primary human bladder smooth muscle cells with SV40 Large T antigen.
Immortalized cells were controlled passaging side by side with the primary cells. Primary cells go into senescence after the 4th passage while the SV40‐tranduced cells go beyond 30 passages.
Each vial of HBlSMC contains more than 1 million viable cells. Innoprot also offers optimized medium and reagents for the growth of HBlSMC which are quality tested together and guaranteed to give maximum performance as a global solution for in vitro HBlSMC culture.
Size/Quantity: 1 million cells / vial

Cellular models for studying the human urogenital system

Immortalized Human Skeletal Muscle Cells - Homo sapiens/Human

PDF] Strain induced remodeling of urinary bladder smooth muscle
ヒト初代培養細胞の販売、カスタム単離と受託試験
(IM-HASMC) provided by Innoprot have been developed by immortalizing primary human healthy aortic smooth muscle cells with SV40 Large T antigen.,

Immortalized Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells

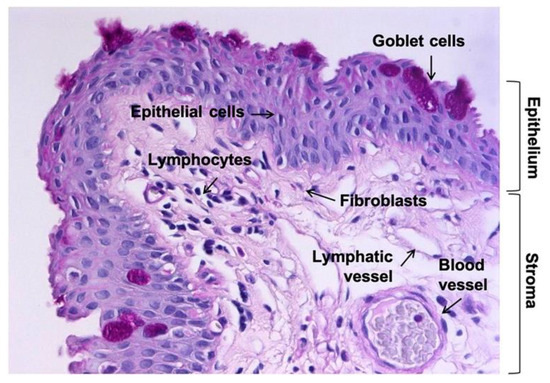
Polyploid Superficial Cells that Maintain the Urothelial Barrier

GAG replenishment therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial
Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text
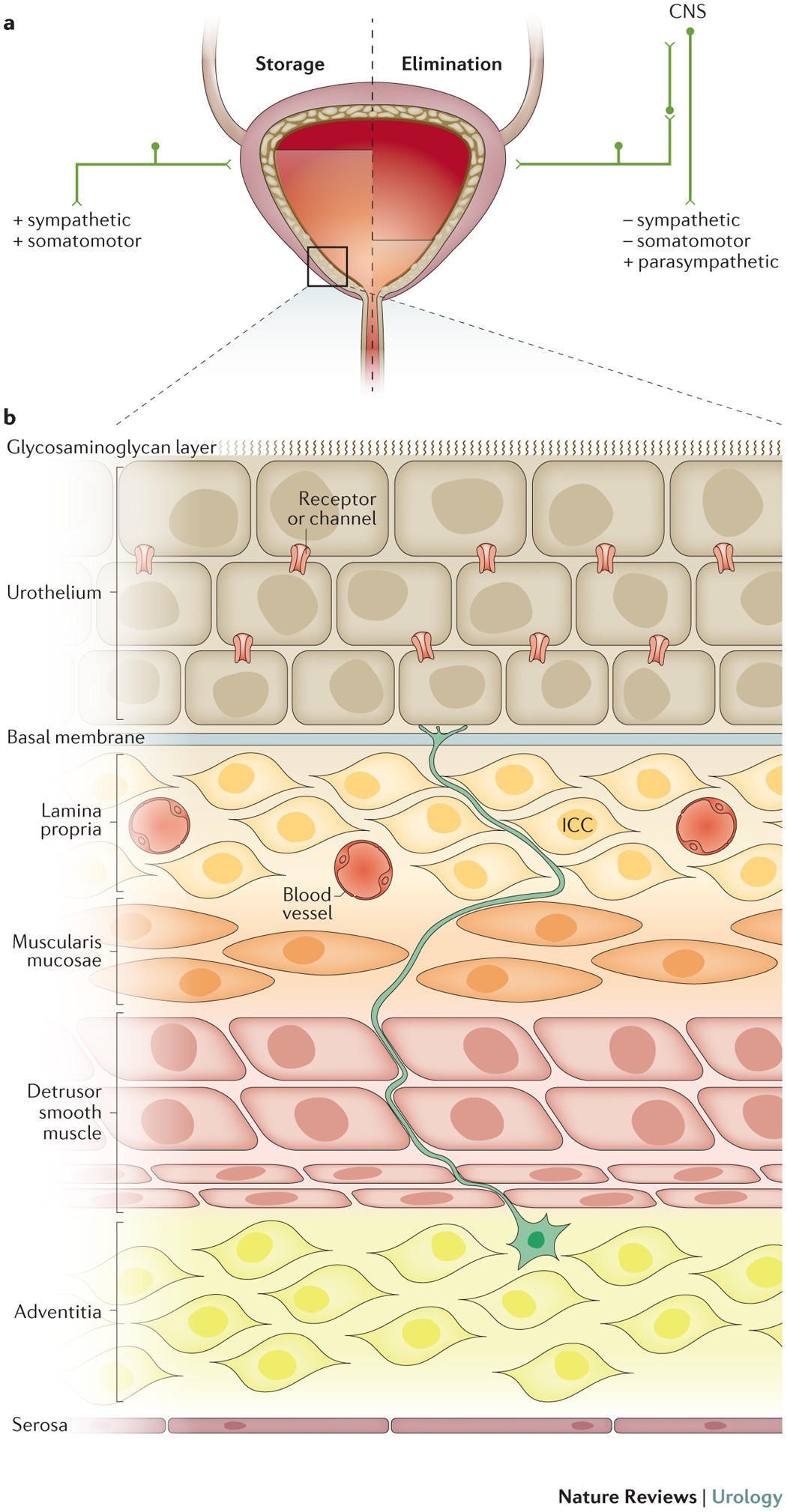
Receptors, channels, and signalling in the urothelial sensory