By A Mystery Man Writer
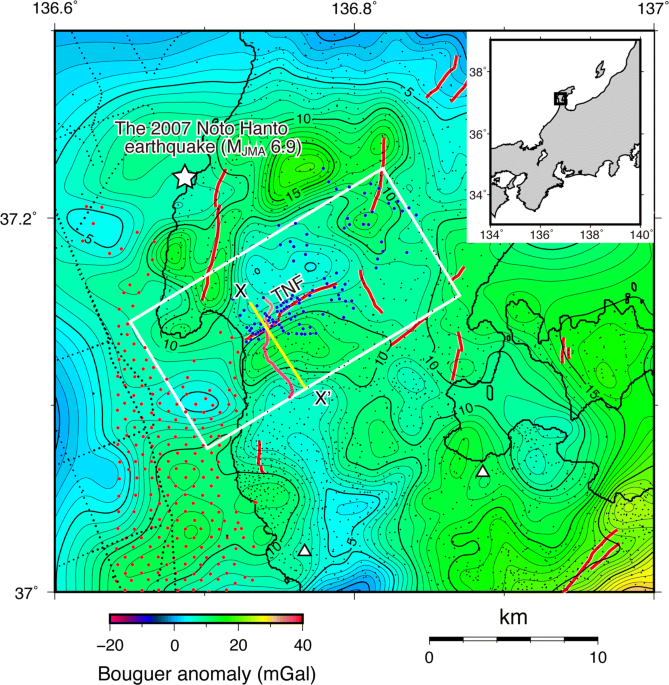
Gravity gradient tensor analysis has been a powerful tool for investigating subsurface structures and recently its application to a two-dimensional fault structure has been developed. To elucidate the faulting type and spatial extent, specifically the continuity and the size, of the subsurface fault structure of an active fault through gravity gradient tensor analysis, we analyzed Bouguer anomalies, which were composed of dense gravity measurement data over the land and seafloor, and indices calculated from a gravity gradient tensor around the Togi-gawa Nangan fault (TNF), Noto Peninsula, central Japan. The features of Bouguer anomalies and their first horizontal and vertical derivatives demonstrate clearly that the TNF is a reverse fault dipping to the southeast. Furthermore, the combination of those derivatives and the dimensionality index revealed that the spatial extent of the subsurface fault structure is coincident with that of the surface fault trace and that it shows no evidence of connecting the TNF with surrounding active faults. Furthermore, the dip angle of the subsurface fault structure was estimated as 45°–60° from the minimum eigenvectors of the gravity gradient tensor. We confirmed that this result is coincident with the dip angle estimated using the two-dimensional Talwani’s method. This high dip angle as a reverse fault suggests that the TNF has experienced inversion tectonics.
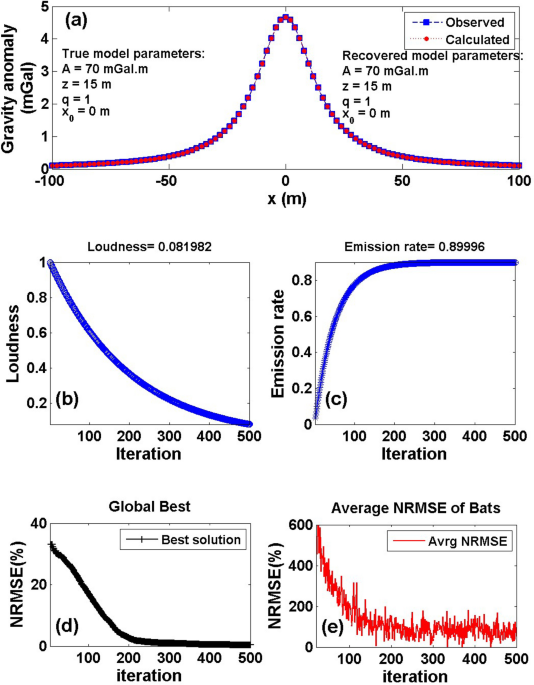
Source parameters estimation from gravity data using Bat algorithm with application to geothermal and volcanic activity studies

First column the original noise-free image and the noisy image. Second

PDF) Continuity, segmentation and faulting type of active fault zones of the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake inferred from analyses of a gravity gradient tensor
A free-geometry geodynamic modelling of surface gravity changes using Growth-dg software

Source parameters estimation from gravity data using Bat algorithm with application to geothermal and volcanic activity studies
SE - Sequential inversion of GOCE satellite gravity gradient data and terrestrial gravity data for the lithospheric density structure in the North China Craton
NeurIPS 2023
Quaternary, Free Full-Text

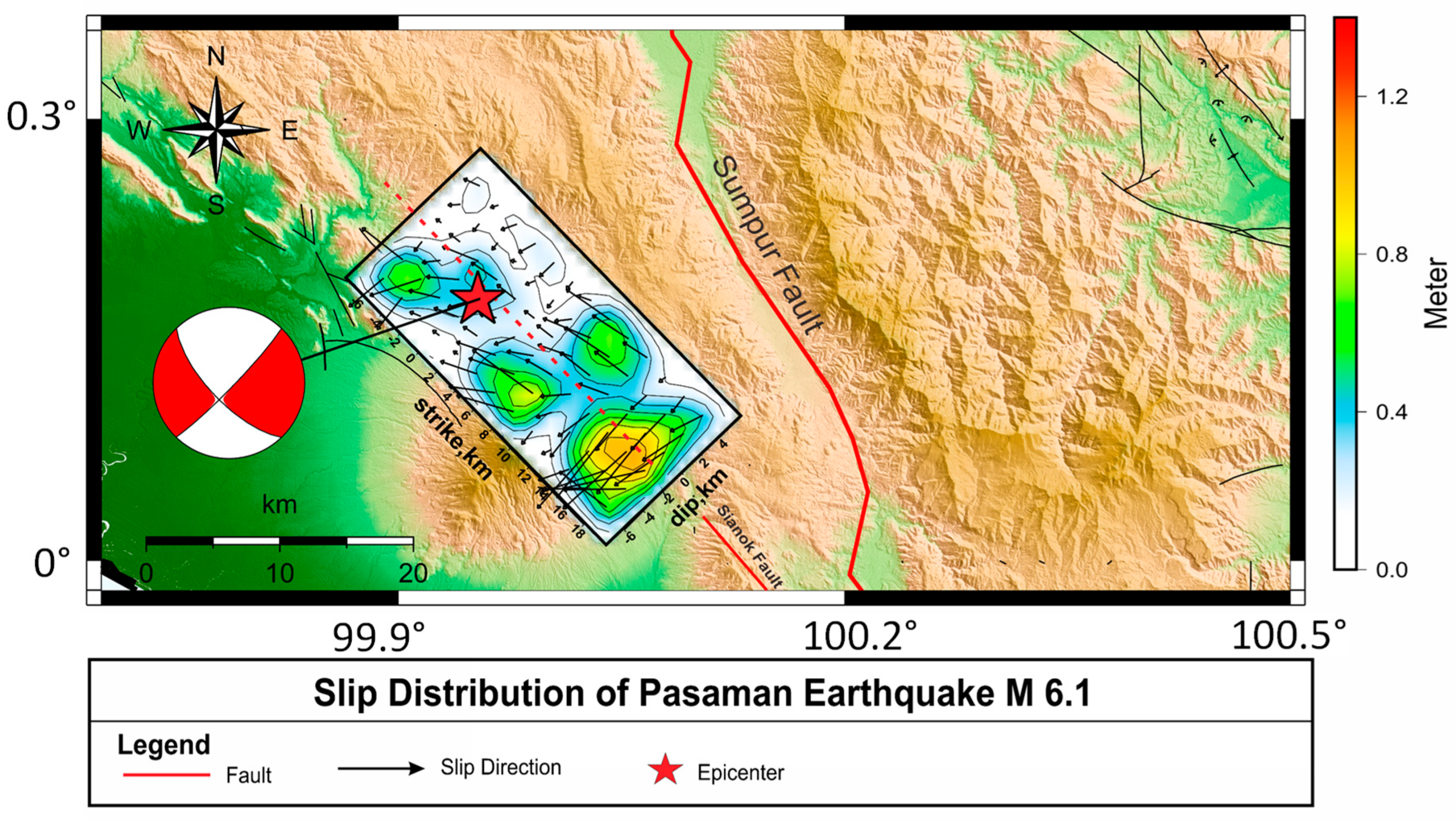
PDF) The 2022 Mw 6.1 Pasaman Barat, Indonesia Earthquake, Confirmed the Existence of the Talamau Segment Fault Based on Teleseismic and Satellite Gravity Data

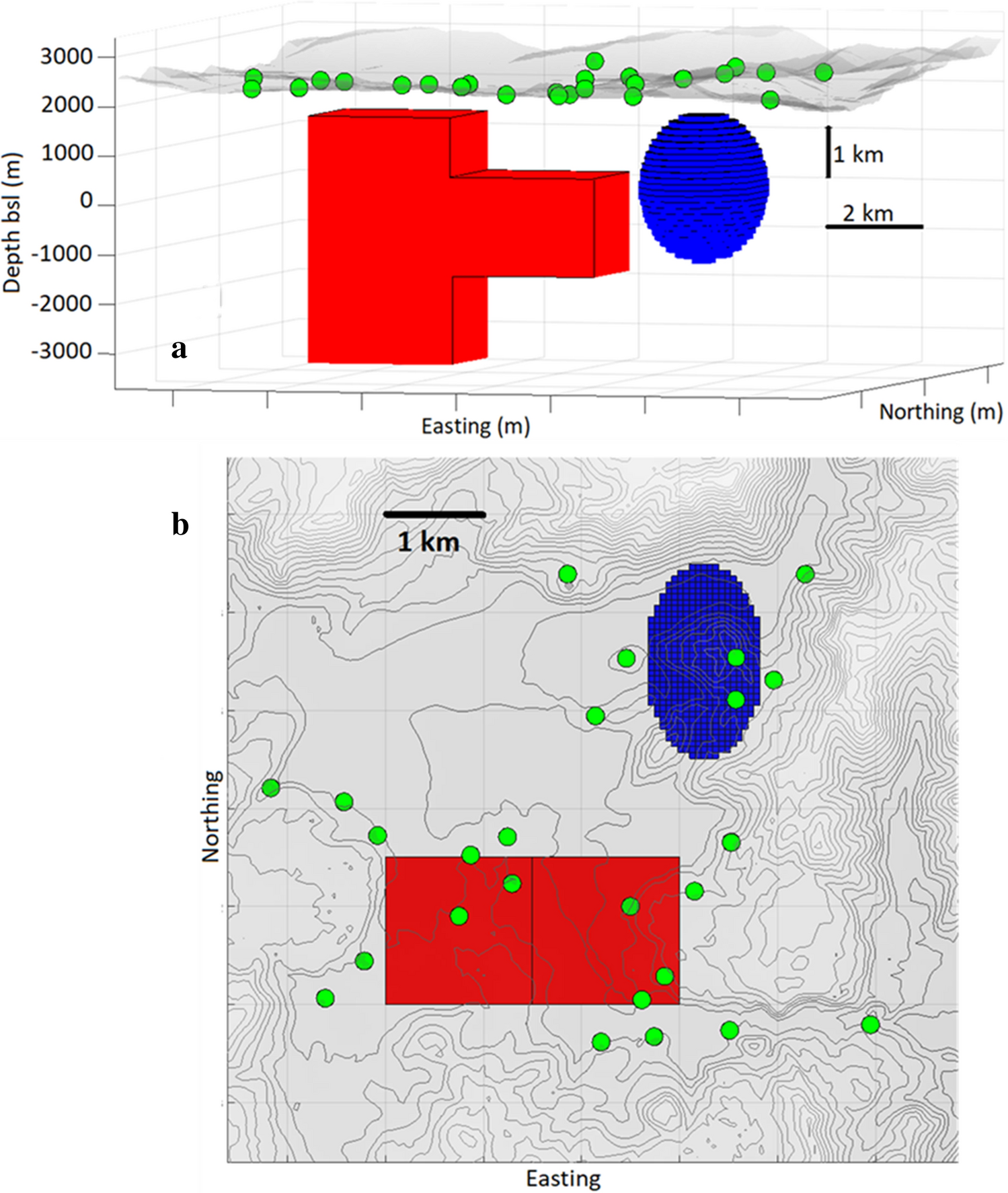
Model of subsurface structures. Here, rectangular causative body of

Delaware basin model quantifies SWD pressure effects
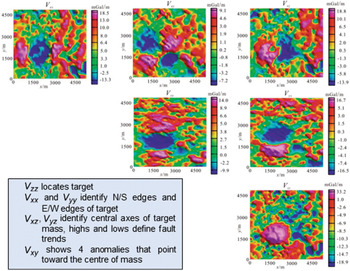
Full Tensor Gradiometry (Chapter 5) - Integration of Geophysical Technologies in the Petroleum Industry

Stress analysis shows slight increase in seismic hazard near Zagreb